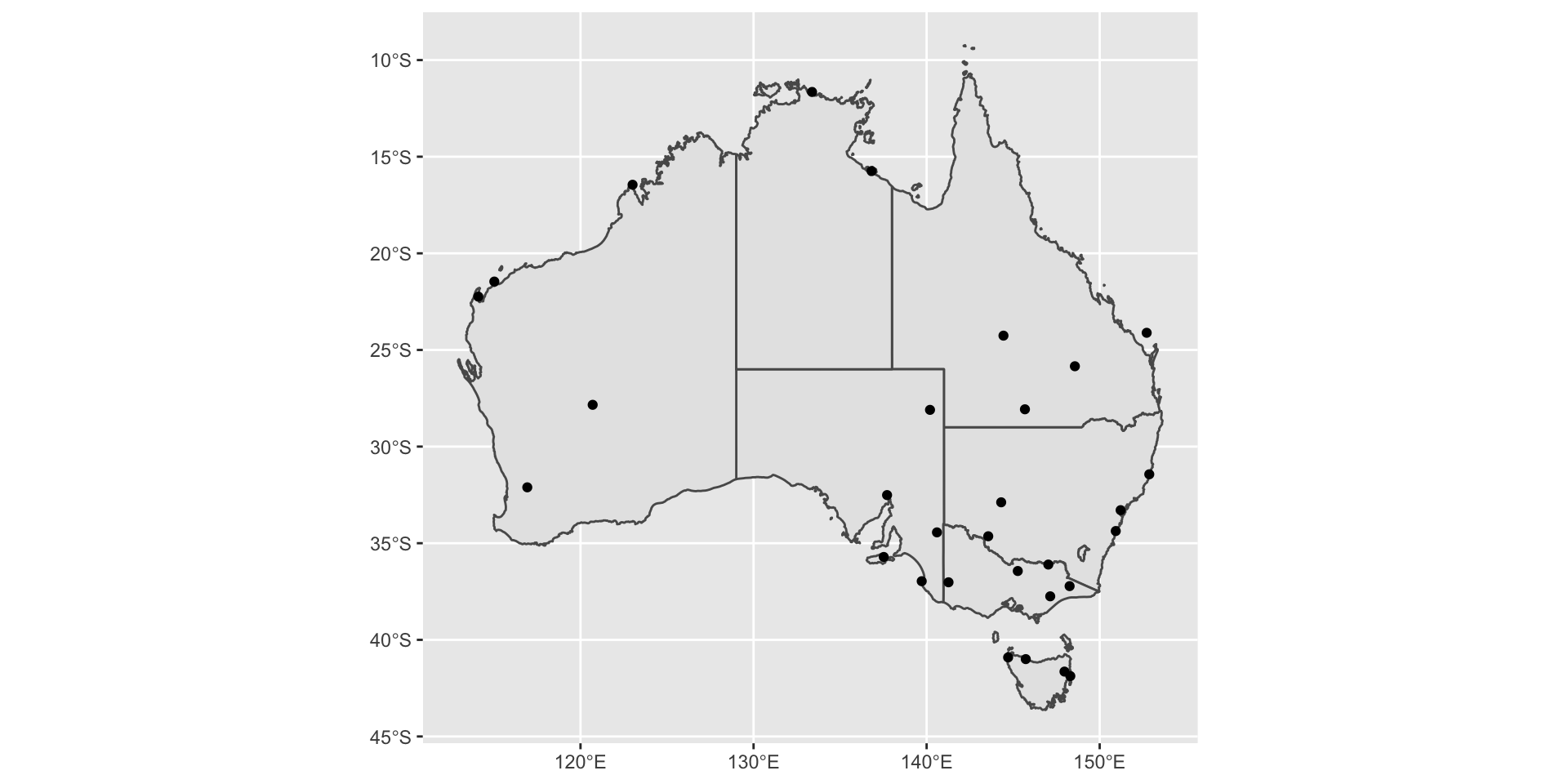
Switching between space and time: Spatio-temporal analysis with
cubble
2022-09-27
Hi!
A 3rd year PhD student in the Department of Econometrics and Business Statistics, Monash University
My research centers on exploring multivariate spatio-temporal data with data wrangling and visualisation tool.
Roadmap
- Follow along with the slides at https://sherryzhang-rladiesmelb2022.netlify.app
- Go to the slide repo to run the code in the
index.Ryourself
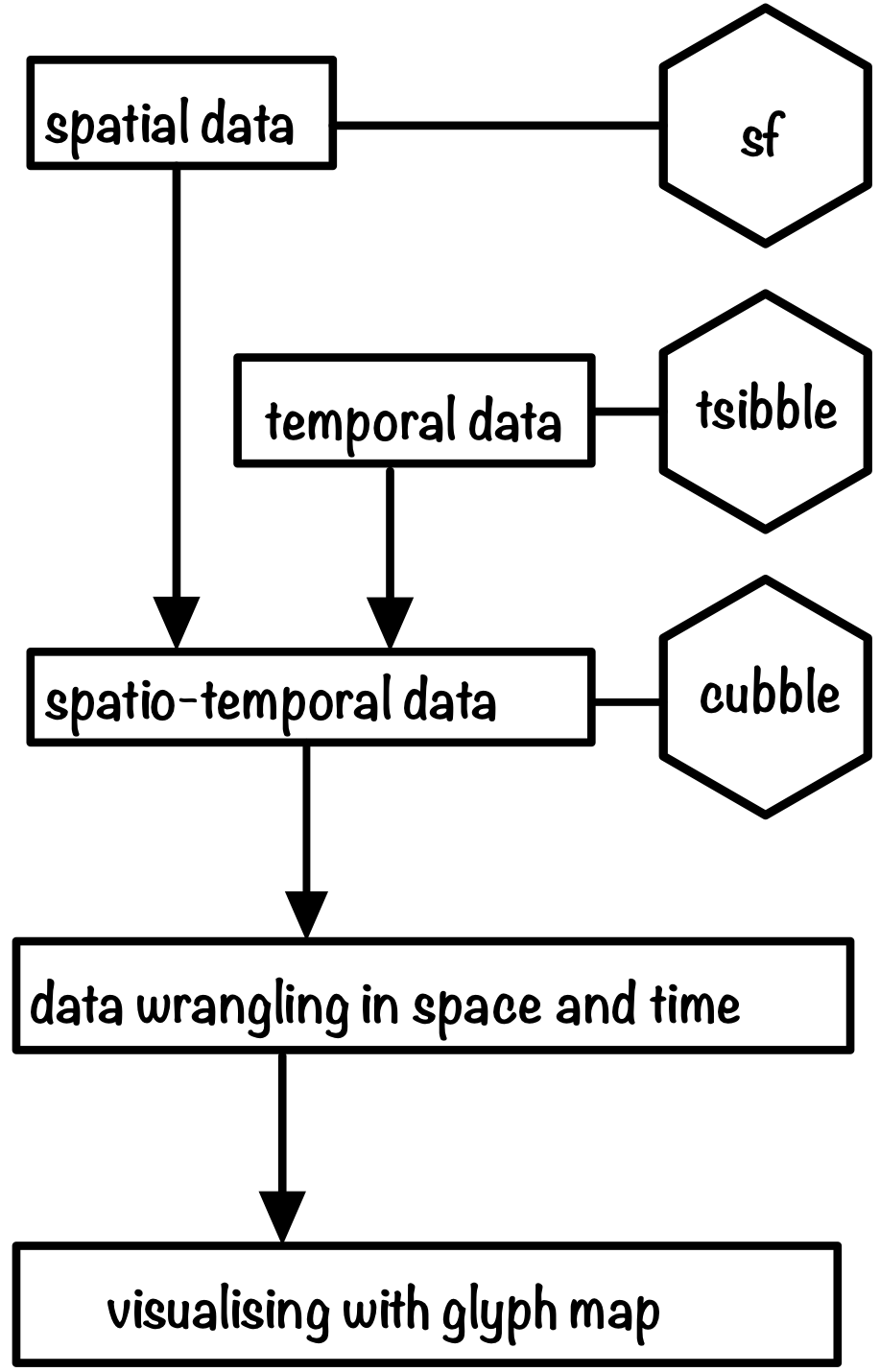
Spatio-temporal data
People can talk about a whole range of differnt things when they only refer to their data as spatio-temporal!
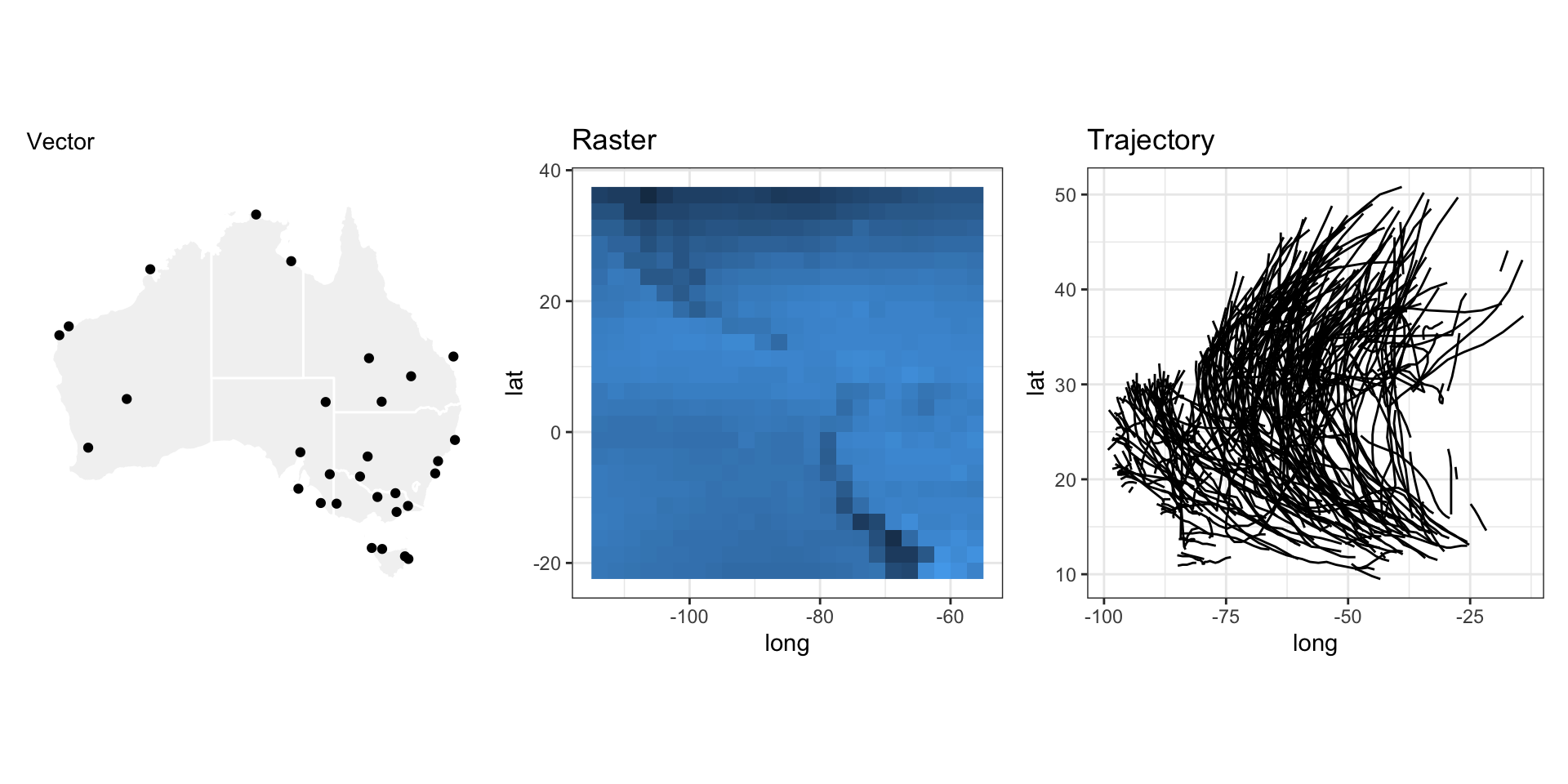
The focus of today will be on vector data
Examples of vector data
Physical sensors that measure the temperature, rainfall, wind speed & direction, water level, etc
A recent blog post on Vector Data Cubes by Edzer Pebesma
Represent spatial data in R?
- A pair of longitude/ latitude (
stations_dt)
# A tibble: 30 × 6
id long lat elev name wmo_id
<chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <chr> <dbl>
1 ASN00060139 153. -31.4 4.2 port macquarie airport aws 94786
2 ASN00068228 151. -34.4 10 bellambi aws 94749
# … with 28 more rows- Simple features with
sf(stations_sf)
Simple feature collection with 30 features and 4 fields
Geometry type: POINT
Dimension: XY
Bounding box: xmin: 114.0967 ymin: -41.8739 xmax: 152.8655 ymax: -11.6502
Geodetic CRS: GDA94
# A tibble: 30 × 5
id elev name wmo_id geometry
<chr> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <POINT [°]>
1 ASN00060139 4.2 port macquarie airport aws 94786 (152.8655 -31.4336)
2 ASN00068228 10 bellambi aws 94749 (150.9291 -34.3691)
# … with 28 more rowsGeometrical operations with sf
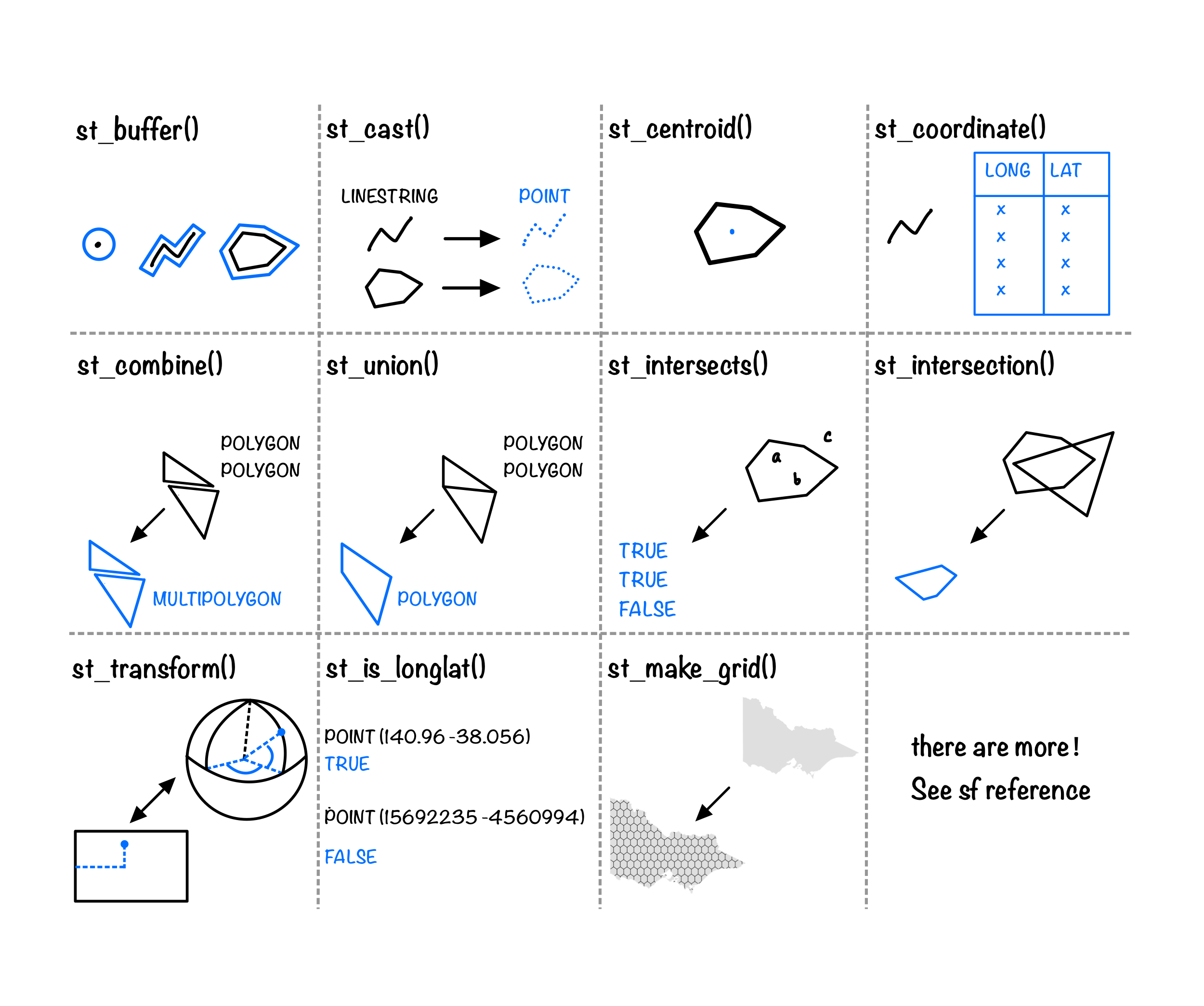
Ploting an sf object
Look into an sf object - POINTS
Simple feature collection with 2 features and 6 fields
Geometry type: POINT
Dimension: XY
Bounding box: xmin: 150.9291 ymin: -34.3691 xmax: 152.8655 ymax: -31.4336
Geodetic CRS: GDA94
# A tibble: 2 × 7
id lat long elev name wmo_id geometry
<chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <POINT [°]>
1 ASN00060139 -31.4 153. 4.2 port macquarie… 94786 (152.8655 -31.4336)
2 ASN00068228 -34.4 151. 10 bellambi aws 94749 (150.9291 -34.3691)Geometry set for 2 features
Geometry type: POINT
Dimension: XY
Bounding box: xmin: 150.9291 ymin: -34.3691 xmax: 152.8655 ymax: -31.4336
Geodetic CRS: GDA94
POINT (152.8655 -31.4336)
POINT (150.9291 -34.3691)POINT (152.8655 -31.4336)Look into an sf object - POINTS (2)
The point sfg is a paired vector with special class labels
POINT (152.8655 -31.4336)[1] "double"$class
[1] "XY" "POINT" "sfg" [1] 152.8655 -31.4336The POINT (152.8655 -31.4336) format is called well-known text, which is a human-readable encoding used by sf
Look into an sf object - POINTS (3)
The sfc is a list of sfg with special attributes
Geometry set for 1 feature
Geometry type: POINT
Dimension: XY
Bounding box: xmin: 152.8655 ymin: -31.4336 xmax: 152.8655 ymax: -31.4336
Geodetic CRS: GDA94
POINT (152.8655 -31.4336)
POINT (150.9291 -34.3691)[1] "list"[1] "class" "precision" "bbox" "crs" "n_empty" [[1]]
POINT (152.8655 -31.4336)
[[2]]
POINT (150.9291 -34.3691)Other geoms (1/3) - LINESTRING
The linestring sfg is a matrix of paired doubles
LINESTRING (149.2317 -35.222, 149.2716 -35.2708, 149.3153 -35.27623, 149.3972 -35.32425, 149.3363 -35.33988, 149.2493 -35.33013, 149.2045 -35.34761, 149.1464 -35.4153, 149.1352, ...)[1] "double" [,1] [,2]
[1,] 149.2317 -35.22200
[2,] 149.2716 -35.27080
[3,] 149.3153 -35.27623
[4,] 149.3972 -35.32425
[5,] 149.3363 -35.33988
[6,] 149.2493 -35.33013
[7,] 149.2045 -35.34761
[8,] 149.1464 -35.41530
[9,] 149.1352 -35.45369
[10,] 149.1516 -35.49320
[11,] 149.1325 -35.54950
[12,] 149.1405 -35.58829
[13,] 149.0781 -35.58642
[14,] 149.0950 -35.67682
[15,] 149.1094 -35.69659
[16,] 149.0907 -35.76562
[17,] 149.1011 -35.80506
[18,] 149.0488 -35.92041
[19,] 149.0122 -35.89970
[20,] 148.9584 -35.89179
[21,] 148.9127 -35.85546
[22,] 148.8894 -35.72272
[23,] 148.8347 -35.74051
[24,] 148.7884 -35.69781
[25,] 148.7985 -35.66698
[26,] 148.7689 -35.60426
[27,] 148.7628 -35.49550
[28,] 148.7858 -35.40891
[29,] 148.8087 -35.38246
[30,] 148.7935 -35.33912
[31,] 148.8101 -35.30745
[32,] 149.1209 -35.12442
[33,] 149.1891 -35.16552
[34,] 149.1903 -35.19435
[35,] 149.2317 -35.22200Other geoms (2/3) - POLYGONS
POLYGON sfg is a list where each element is a matrix of paired vectors
POLYGON ((149.2317 -35.222, 149.2716 -35.2708, 149.3153 -35.27623, 149.3972 -35.32425, 149.3363 -35.33988, 149.2493 -35.33013, ...))[1] "list"[[1]]
[,1] [,2]
[1,] 149.2317 -35.22200
[2,] 149.2716 -35.27080
[3,] 149.3153 -35.27623
[4,] 149.3972 -35.32425
[5,] 149.3363 -35.33988
[6,] 149.2493 -35.33013
[7,] 149.2045 -35.34761
[8,] 149.1464 -35.41530
[9,] 149.1352 -35.45369
[10,] 149.1516 -35.49320
[11,] 149.1325 -35.54950
[12,] 149.1405 -35.58829
[13,] 149.0781 -35.58642
[14,] 149.0950 -35.67682
[15,] 149.1094 -35.69659
[16,] 149.0907 -35.76562
[17,] 149.1011 -35.80506
[18,] 149.0488 -35.92041
[19,] 149.0122 -35.89970
[20,] 148.9584 -35.89179
[21,] 148.9127 -35.85546
[22,] 148.8894 -35.72272
[23,] 148.8347 -35.74051
[24,] 148.7884 -35.69781
[25,] 148.7985 -35.66698
[26,] 148.7689 -35.60426
[27,] 148.7628 -35.49550
[28,] 148.7858 -35.40891
[29,] 148.8087 -35.38246
[30,] 148.7935 -35.33912
[31,] 148.8101 -35.30745
[32,] 149.1209 -35.12442
[33,] 149.1891 -35.16552
[34,] 149.1903 -35.19435
[35,] 149.2317 -35.22200And lastly … MULTIPOLYGONS!
MULTIPOLYGON sfg is a nested list where each list element can contain multiple matrices of paired vectors
MULTIPOLYGON (((145.2859 -38.3962, 145.2903 -38.28367, 145.4109 -38.37078, 145.2859 -38.3962)), ((140.9657 -38.05599, 140.9739 -37.46209, 140.9693 -36.79305, 140.9631 -35.74853, 140.9656 -35.00826, 140.9617 -34.09582, ...)))[1] "list"[1] 2[[1]]
[[1]][[1]]
[,1] [,2]
[1,] 145.2859 -38.39620
[2,] 145.2903 -38.28367
[3,] 145.4109 -38.37078
[4,] 145.2859 -38.39620
[[2]]
[[2]][[1]]
[,1] [,2]
[1,] 140.9657 -38.05599
[2,] 140.9739 -37.46209
[3,] 140.9693 -36.79305
[4,] 140.9631 -35.74853
[5,] 140.9656 -35.00826
[6,] 140.9617 -34.09582
[7,] 141.0089 -34.04466
[8,] 141.2610 -34.07898
[9,] 141.3576 -34.11069
[10,] 141.5176 -34.20645
[11,] 141.7049 -34.09569
[12,] 141.8424 -34.13253
[13,] 141.8991 -34.11149
[14,] 142.0745 -34.13049
[15,] 142.0821 -34.17299
[16,] 142.2203 -34.18167
[17,] 142.2385 -34.30782
[18,] 142.3337 -34.33930
[19,] 142.3684 -34.52709
[20,] 142.4347 -34.57615
[21,] 142.5262 -34.75981
[22,] 142.6968 -34.72016
[23,] 142.6995 -34.60315
[24,] 142.7635 -34.59674
[25,] 143.0400 -34.70251
[26,] 143.1041 -34.69400
[27,] 143.3515 -34.79600
[28,] 143.3196 -34.96870
[29,] 143.3470 -35.10478
[30,] 143.3964 -35.19311
[31,] 143.5639 -35.20263
[32,] 143.5637 -35.31612
[33,] 143.6423 -35.40104
[34,] 143.7465 -35.38860
[35,] 143.8666 -35.48032
[36,] 144.0479 -35.55617
[37,] 144.1175 -35.62593
[38,] 144.3757 -35.80121
[39,] 144.4082 -35.90422
[40,] 144.5833 -36.03903
[41,] 144.8058 -36.12384
[42,] 144.9236 -35.98895
[43,] 144.9750 -35.88343
[44,] 145.0729 -35.82776
[45,] 145.2465 -35.83041
[46,] 145.3524 -35.86580
[47,] 145.5340 -35.80529
[48,] 145.6847 -35.93075
[49,] 145.7934 -35.98282
[50,] 145.9080 -35.95356
[51,] 145.9891 -36.01308
[52,] 146.2618 -36.01580
[53,] 146.3877 -36.03527
[54,] 146.4143 -35.97545
[55,] 146.5179 -35.96006
[56,] 146.6870 -36.04082
[57,] 146.8363 -36.08219
[58,] 147.0162 -36.08950
[59,] 147.1372 -36.02862
[60,] 147.2043 -36.04989
[61,] 147.3522 -36.03229
[62,] 147.4043 -35.94356
[63,] 147.4986 -35.94664
[64,] 147.5552 -36.00321
[65,] 147.7084 -35.92854
[66,] 147.9140 -35.99795
[67,] 147.9976 -36.04777
[68,] 148.0289 -36.14008
[69,] 148.0383 -36.36556
[70,] 148.1247 -36.46484
[71,] 148.1244 -36.55098
[72,] 148.2174 -36.59885
[73,] 148.1851 -36.69222
[74,] 148.1949 -36.79625
[75,] 149.1998 -37.20119
[76,] 149.9763 -37.50503
[77,] 149.7393 -37.58451
[78,] 149.6747 -37.68584
[79,] 149.4948 -37.76847
[80,] 149.2516 -37.78179
[81,] 148.8087 -37.78642
[82,] 148.6260 -37.80814
[83,] 148.3662 -37.80395
[84,] 148.1792 -37.83164
[85,] 147.7884 -37.95525
[86,] 147.4672 -38.15915
[87,] 147.0672 -38.47512
[88,] 146.9320 -38.59602
[89,] 146.7857 -38.64632
[90,] 146.4438 -38.69492
[91,] 146.2675 -38.68791
[92,] 146.1856 -38.74344
[93,] 146.2656 -38.80531
[94,] 146.2919 -38.90428
[95,] 146.4170 -38.84892
[96,] 146.4873 -38.90615
[97,] 146.4367 -38.97907
[98,] 146.4209 -39.12585
[99,] 146.2739 -38.99612
[100,] 146.1842 -38.86951
[101,] 146.0632 -38.81177
[102,] 145.9189 -38.90688
[103,] 145.8715 -38.77944
[104,] 145.7308 -38.64813
[105,] 145.5647 -38.65419
[106,] 145.4237 -38.53648
[107,] 145.4329 -38.42871
[108,] 145.5525 -38.35457
[109,] 145.4883 -38.23615
[110,] 145.3442 -38.21445
[111,] 145.2550 -38.23743
[112,] 145.1299 -38.39045
[113,] 145.0257 -38.47967
[114,] 144.9244 -38.49740
[115,] 144.8369 -38.37040
[116,] 144.9750 -38.32697
[117,] 145.1213 -38.13339
[118,] 145.0906 -38.01495
[119,] 145.0307 -37.99351
[120,] 144.9638 -37.85576
[121,] 144.8085 -37.88033
[122,] 144.6502 -38.00202
[123,] 144.4874 -38.07828
[124,] 144.3979 -38.07382
[125,] 144.3561 -38.13840
[126,] 144.4807 -38.16449
[127,] 144.6318 -38.10734
[128,] 144.7197 -38.14612
[129,] 144.6142 -38.29214
[130,] 144.4357 -38.28130
[131,] 144.2516 -38.38841
[132,] 144.0365 -38.47578
[133,] 143.9731 -38.56636
[134,] 143.8421 -38.67908
[135,] 143.6854 -38.73536
[136,] 143.5557 -38.85494
[137,] 143.3569 -38.75435
[138,] 143.2203 -38.76029
[139,] 143.0217 -38.62625
[140,] 142.8611 -38.60563
[141,] 142.5633 -38.42200
[142,] 142.3722 -38.34942
[143,] 142.1482 -38.38969
[144,] 141.8849 -38.26629
[145,] 141.7420 -38.25311
[146,] 141.5992 -38.32107
[147,] 141.5575 -38.42235
[148,] 141.4067 -38.36934
[149,] 141.3574 -38.27460
[150,] 141.2278 -38.17065
[151,] 140.9657 -38.05599Geometry types - summary
The
sf,sfc, andsfgobjects have informative header prints but they can be boiled down to basic data structures that we’re already familiar withThere are more than just introduced geometry types: MULTIPOINTS, MULTILINESTRING, etc
In practice, you don’t have to decompose/ manipulate these vectors or matrices manually, existing geometrical operations (
st_*()) and visualisation tools (geom_sf()) will do that for you.
Geometrical operations with sf again

Aggregate time series with tsibble
Time series of weather station data
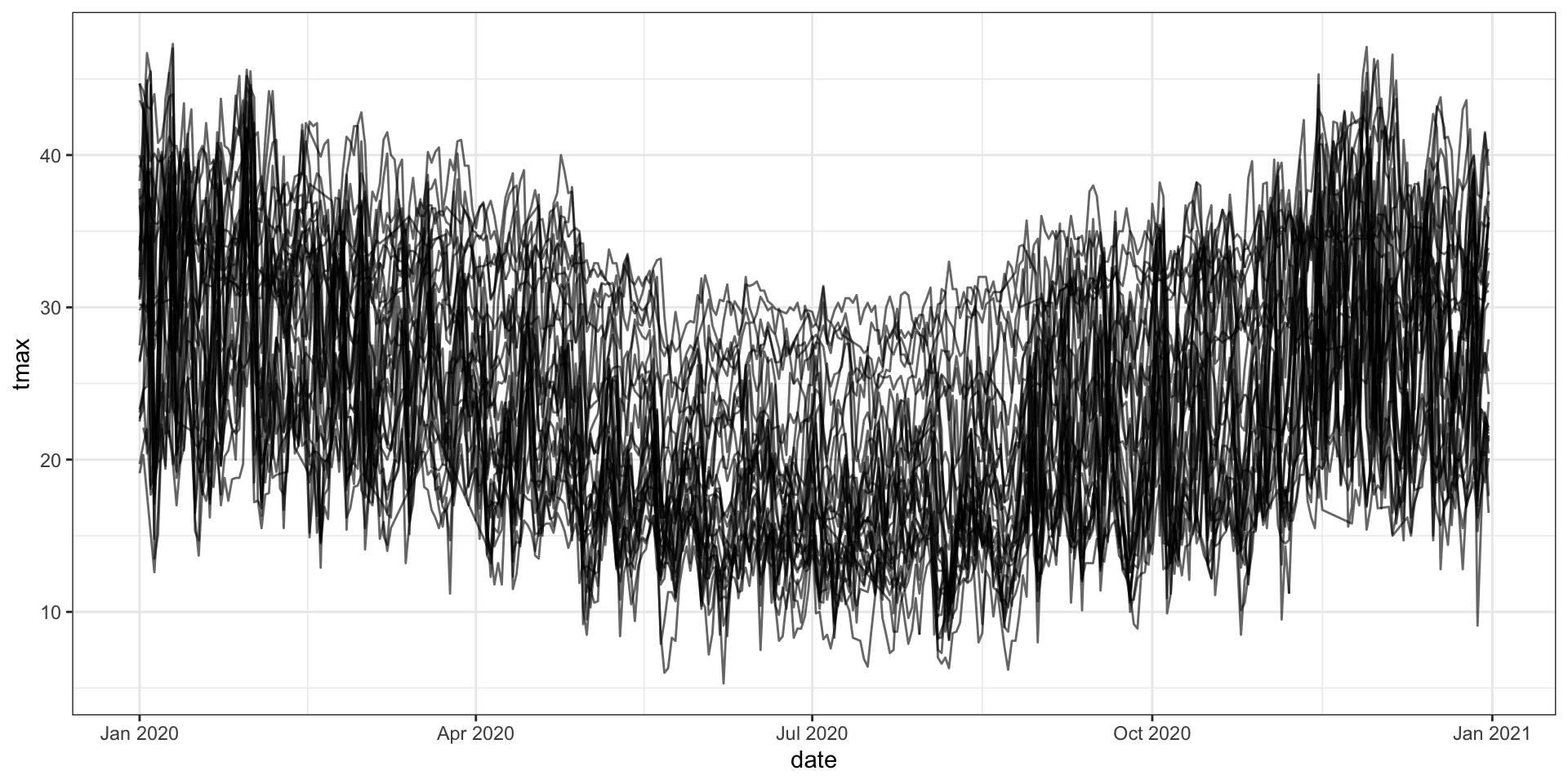
How’s the data quality from BOM?
First cast the data into a tsibble, before using tsibble::count_gaps() for data quality check
# A tibble: 10,632 × 5
id date prcp tmax tmin
<chr> <date> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 ASN00003057 2020-01-01 0 36.7 26.9
2 ASN00003057 2020-01-02 41 34.2 24
3 ASN00003057 2020-01-03 0 35 25.4
4 ASN00003057 2020-01-04 40 29.1 25.4
5 ASN00003057 2020-01-05 1640 27.3 24.3
6 ASN00003057 2020-01-06 1832 29.2 23.2
7 ASN00003057 2020-01-07 42 36 21
8 ASN00003057 2020-01-08 300 31.5 25
9 ASN00003057 2020-01-09 90 32.2 25.3
10 ASN00003057 2020-01-10 0 34 25.9
# … with 10,622 more rows# A tsibble: 10,632 x 5 [1D]
# Key: id [30]
id date prcp tmax tmin
<chr> <date> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 ASN00003057 2020-01-01 0 36.7 26.9
2 ASN00003057 2020-01-02 41 34.2 24
3 ASN00003057 2020-01-03 0 35 25.4
4 ASN00003057 2020-01-04 40 29.1 25.4
5 ASN00003057 2020-01-05 1640 27.3 24.3
6 ASN00003057 2020-01-06 1832 29.2 23.2
7 ASN00003057 2020-01-07 42 36 21
8 ASN00003057 2020-01-08 300 31.5 25
9 ASN00003057 2020-01-09 90 32.2 25.3
10 ASN00003057 2020-01-10 0 34 25.9
# … with 10,622 more rowsHow’s the data quality from BOM?
# A tibble: 112 × 4
id .from .to .n
<chr> <date> <date> <int>
1 ASN00003057 2020-02-17 2020-02-18 2
2 ASN00003057 2020-02-25 2020-03-01 6
3 ASN00003057 2020-03-07 2020-03-09 3
4 ASN00003057 2020-03-11 2020-03-13 3
5 ASN00003057 2020-03-25 2020-03-27 3
# … with 107 more rowsHow’s the data quality from BOM?
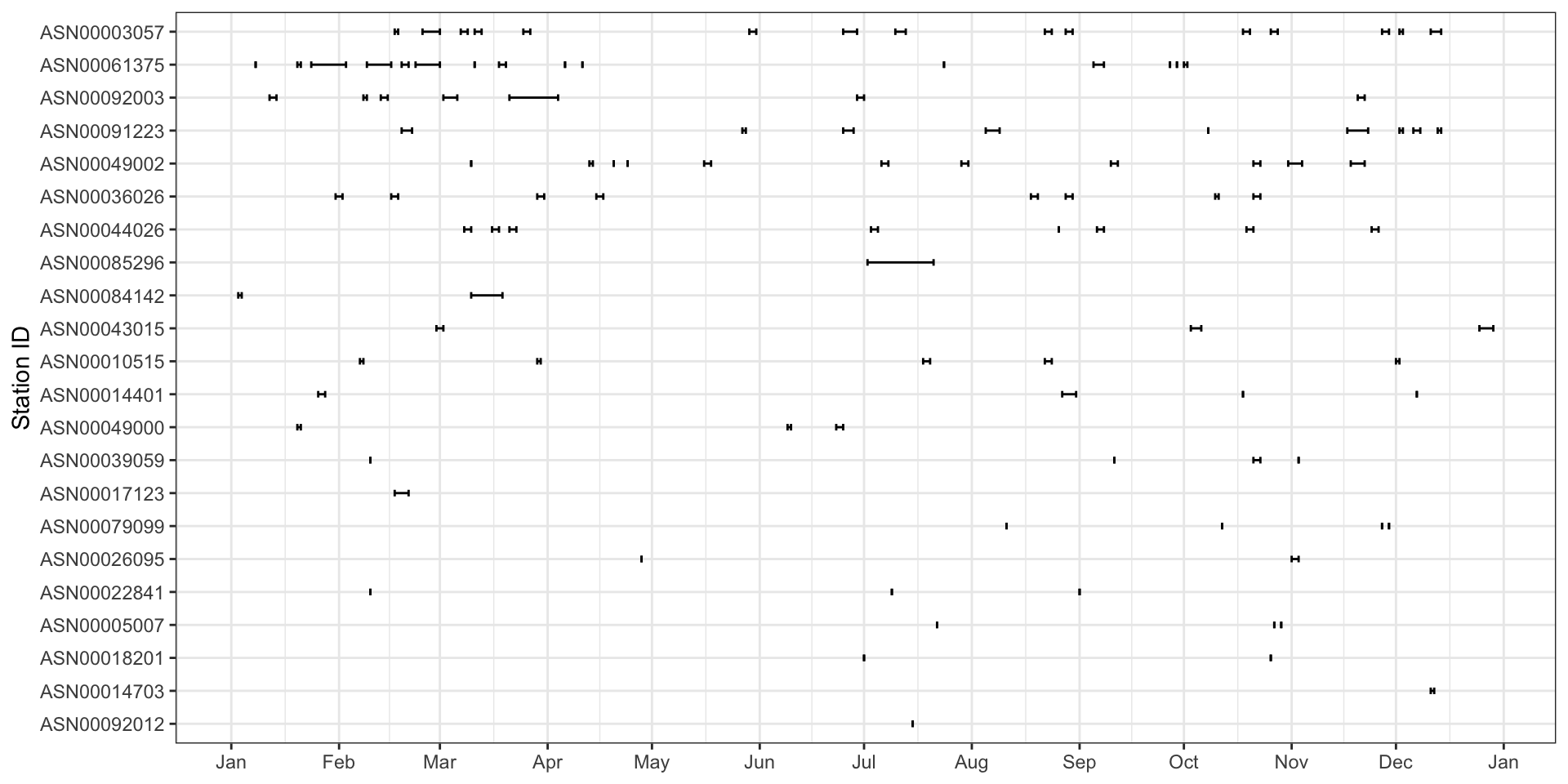
Make the inexplicit NAs explicit
# A tsibble: 271 x 5 [1D]
# Key: id [1]
id date prcp tmax tmin
<chr> <date> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 ASN00003057 2020-02-15 0 33.7 25.5
2 ASN00003057 2020-02-16 0 33.5 28.5
3 ASN00003057 2020-02-19 20 34 24.4
4 ASN00003057 2020-02-20 0 34.1 26.5
5 ASN00003057 2020-02-21 0 34.5 25.7
# … with 266 more rows# A tsibble: 321 x 5 [1D]
# Key: id [1]
id date prcp tmax tmin
<chr> <date> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 ASN00003057 2020-02-15 0 33.7 25.5
2 ASN00003057 2020-02-16 0 33.5 28.5
3 ASN00003057 2020-02-17 NA NA NA
4 ASN00003057 2020-02-18 NA NA NA
5 ASN00003057 2020-02-19 20 34 24.4
# … with 316 more rows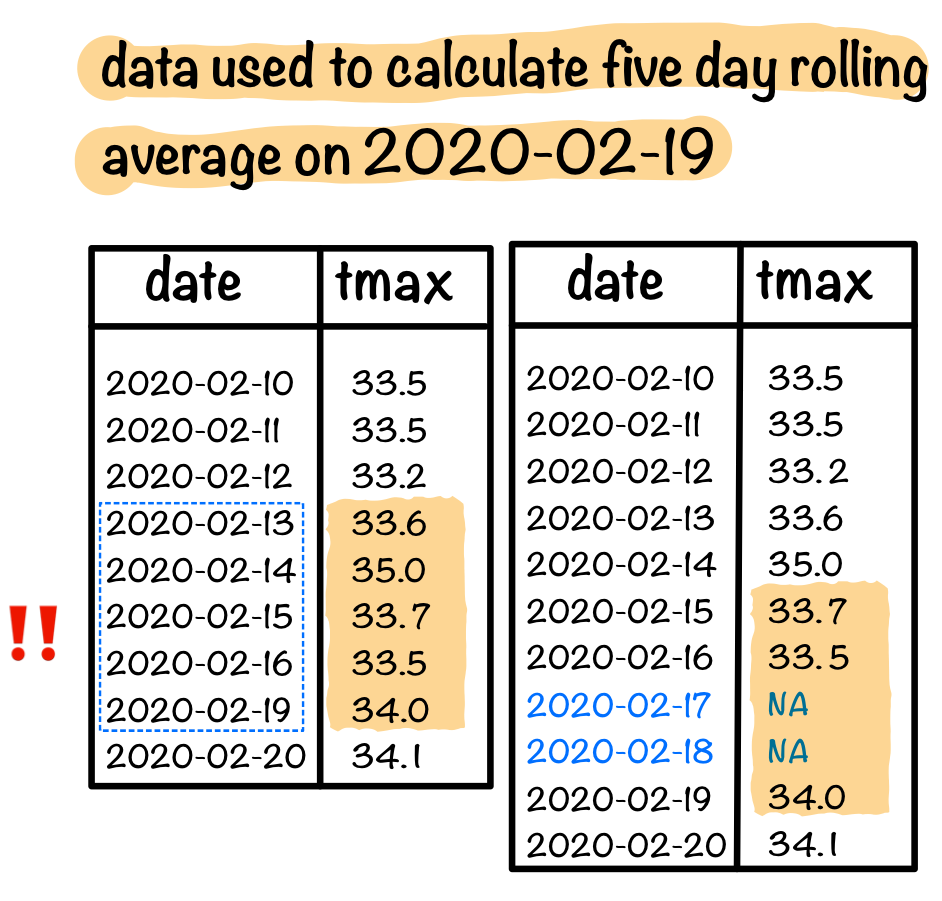
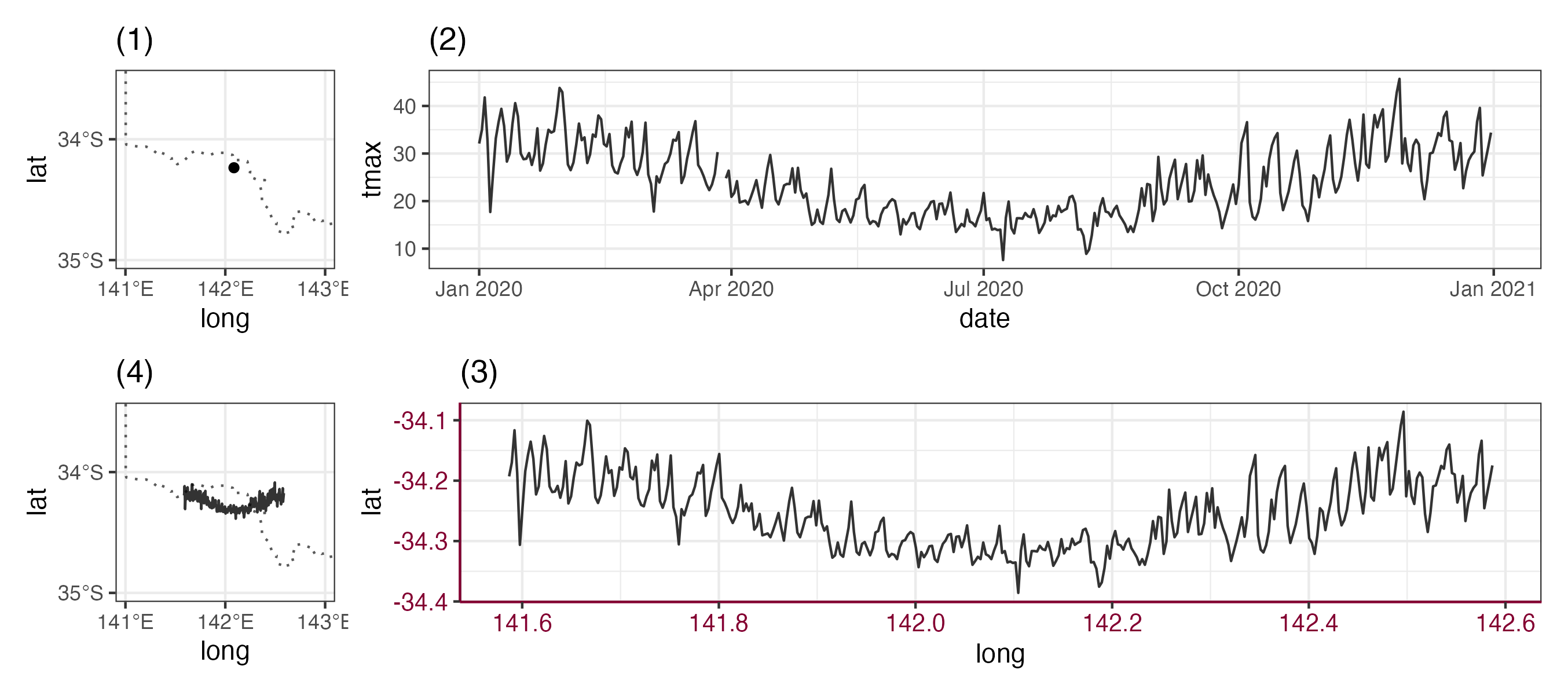
Space and time at the same time with cubble
Goal of today: glyph map
Cubble - a spatio-temporal vector data structure
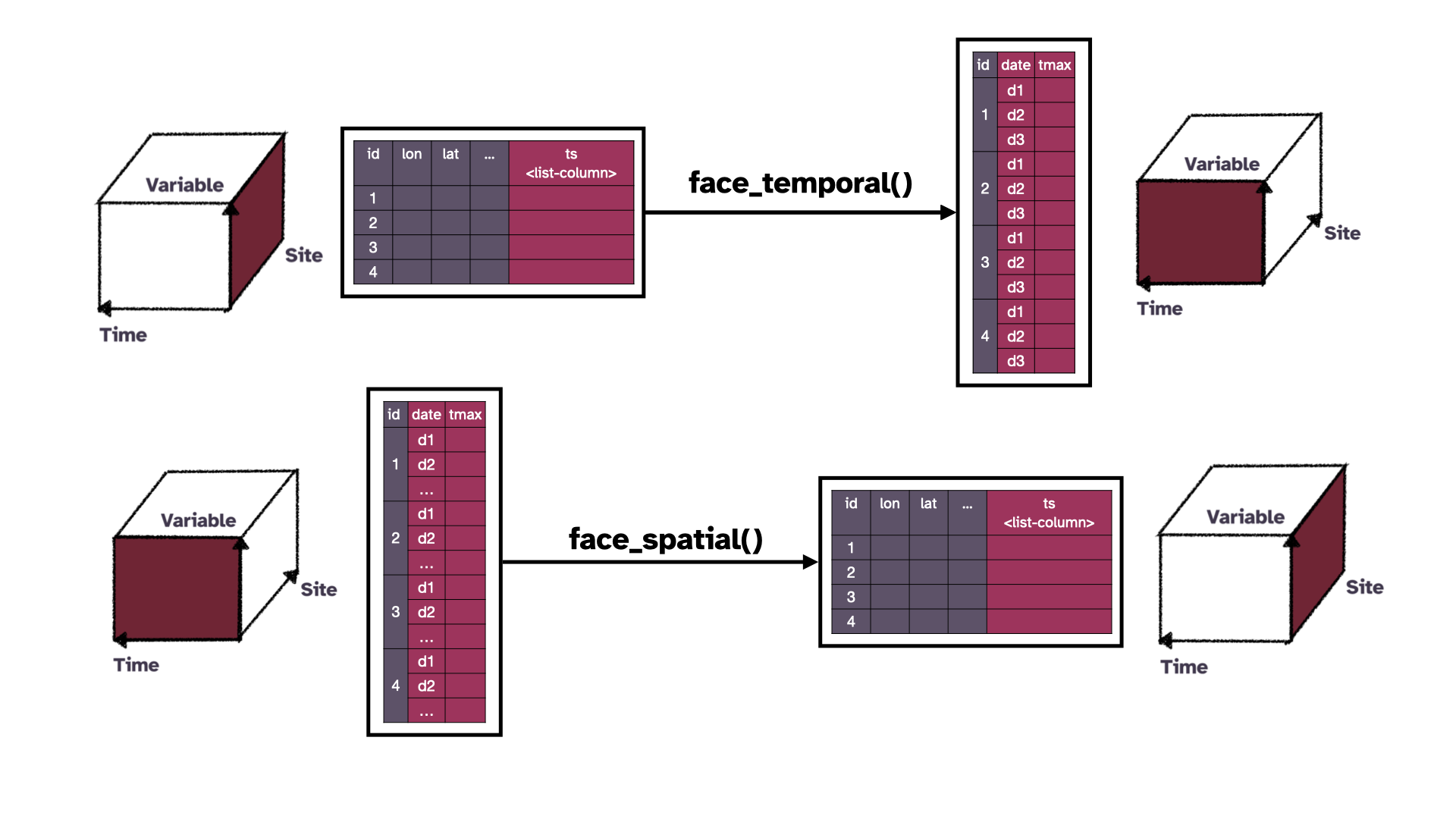
Cast your data into a cubble
(cb <- as_cubble(
list(spatial = stations_sf, temporal = ts),
key = id, index = date, coords = c(long, lat)
))# cubble: id [30]: nested form [sf]
# bbox: [114.09, -41.88, 152.87, -11.65]
# temporal: date [date], prcp [dbl], tmax [dbl], tmin [dbl]
id lat long elev name wmo_id geometry ts
<chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <POINT [°]> <list>
1 ASN00003057 -16.5 123. 7 cygne… 94201 (123.0086 -16.4514) <tibble>
2 ASN00005007 -22.2 114. 5 learm… 94302 (114.0967 -22.2406) <tibble>
3 ASN00005084 -21.5 115. 5 theve… 94303 (115.0197 -21.4606) <tibble>
4 ASN00010515 -32.1 117. 199 bever… 95615 (116.9247 -32.1083) <tibble>
5 ASN00012314 -27.8 121. 497 leins… 95448 (120.7031 -27.8386) <tibble>
6 ASN00014401 -11.7 133. 19.2 warru… 94139 (133.3796 -11.6502) <tibble>
7 ASN00014703 -15.7 137. 12.2 centr… 94248 (136.8192 -15.7426) <tibble>
# … with 23 more rowsSubset on space
Summarise in time
(cb_tm <- cb_space %>%
face_temporal() %>%
group_by(month = lubridate::month(date)) %>%
summarise(tmax = mean(tmax, na.rm = TRUE))
)# cubble: month, id [20]: long form
# bbox: [114.09, -41.65, 152.72, -11.65]
# spatial: lat [dbl], long [dbl], elev [dbl], name [chr], wmo_id [dbl],
# geometry [POINT [°]]
id month tmax
<chr> <dbl> <dbl>
1 ASN00005007 1 38.8
2 ASN00005007 2 37.5
3 ASN00005007 3 38.1
4 ASN00005007 4 35.8
5 ASN00005007 5 28.6
6 ASN00005007 6 26.6
7 ASN00005007 7 27.4
# … with 233 more rowsMove coordinates into time
# cubble: month, id [20]: long form
# bbox: [114.09, -41.65, 152.72, -11.65]
# spatial: lat [dbl], long [dbl], elev [dbl], name [chr], wmo_id [dbl],
# geometry [POINT [°]]
id month tmax long lat
<chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 ASN00005007 1 38.8 114. -22.2
2 ASN00005007 2 37.5 114. -22.2
3 ASN00005007 3 38.1 114. -22.2
4 ASN00005007 4 35.8 114. -22.2
5 ASN00005007 5 28.6 114. -22.2
6 ASN00005007 6 26.6 114. -22.2
7 ASN00005007 7 27.4 114. -22.2
# … with 233 more rowsGlyph map transformation
https://huizezhang-sherry.github.io/cubble/articles/glyph.html
Making your first glyph map
Code
cb <- as_cubble(
list(spatial = stations_sf, temporal = ts),
key = id, index = date, coords = c(long, lat)
)
set.seed(0927)
cb_glyph <- cb %>%
slice_sample(n = 20) %>%
face_temporal() %>%
group_by(month = lubridate::month(date)) %>%
summarise(tmax = mean(tmax, na.rm = TRUE)) %>%
unfold(long, lat)
ggplot() +
geom_sf(data = oz_simp, fill = "grey95", color = "white") +
geom_glyph(
data = cb_glyph,
aes(x_major = long, x_minor = month, y_major = lat, y_minor = tmax),
width = 2, height = 0.7) +
ggthemes::theme_map()
Your Time
Create a cubble object from the spatial and temporal data given
Perform an operation on the space in the nested form
Switch to the long form to summarise the temporal data
Make a glyph map!
Further reading
- Spatial Data Science with application to R: https://r-spatial.org/book/
- sf: https://r-spatial.github.io/sf/index.html
- tsibble: https://tsibble.tidyverts.org/
- cubble: https://huizezhang-sherry.github.io/cubble/
Acknowledgements
The slides are made with Quarto
All the materials used to prepare the slides are available at sherryzhang-RLadiesMelb2022.netlify.app